Table of Contents
The short answer to this question is – yes. Mushrooms are unique in the nutrition they can provide. You get many health benefits by consuming them as food or medicinal supplement.
Mushrooms are Fungi
Mushrooms are higher fungal species. They are more related to animals than plants. There are 140,000 species of mushrooms in the world.
Only 2000 are safe for human consumption. We know of 650 mushroom species that have medicinal value.
Mushrooms grow all around the world. They need high humidity and moderate temperatures. You will find them growing in pastures or forests in the soil, on live trees, and on dead and decaying wood.
Mushrooms are ectomycorrhiza that grows above ground. The parts which we eat are their fruiting bodies.
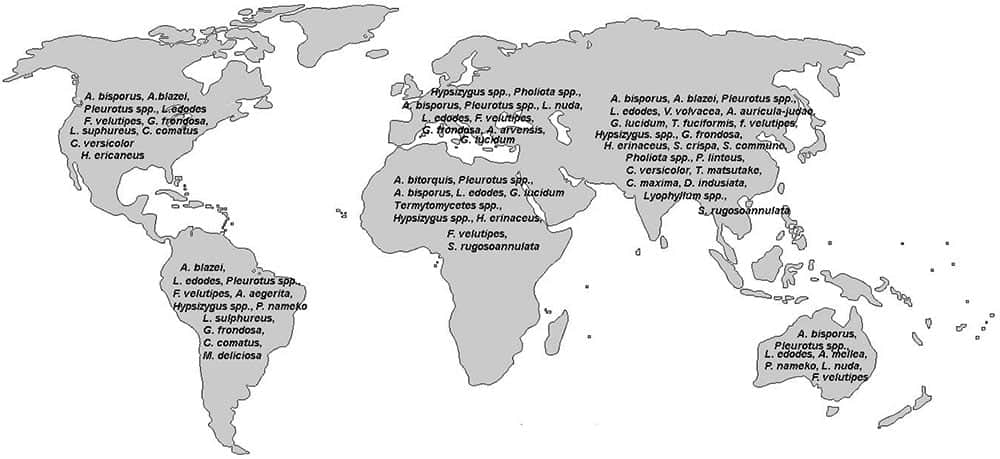
(Image credits: Molecules 2015, 20(10), 19489-19525; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201019489)
Know Your Mushrooms
Mushrooms come in different shapes, sizes, and colors. It is difficult to separate mushrooms as edible and medicinal. All could be beneficial for your health.
There are two major groups of edible fungus:
- Basidiomycetes
- Ascomycetes
Basidiomycetes
You will find cultivated and wild mushrooms in this group. Basidiomycetes include mushrooms, boletes, and bracket fungi.
- Button Mushrooms: Many cultivated mushrooms are in this group. They include white button, portobello, and cremini. The scientific name used for them is Agaricus bisporus
- Shiitake: This group is Lentinus edodes. They grow in East Asia and have medicinal properties
- Oyster: It is one of the most grown edible mushrooms. It belongs to the species Pleurotus ostreatus
- Enoki: Popular in East Asian cuisine. Its scientific name is Flammulina ostreatus
Ascomycetes
The mushrooms in this group are morels (Morchella esculenta) and chanterelles (Cantharellus cibarius). Cultivation of these types is not common. People gather them from the wild and sell them.
Check the map in Figure 1, to find out the mushrooms common in your area.
Nutritional Value of Mushrooms
People have used mushrooms as food and as folklore medicine for thousands of years.
Consider making them a part of your diet because of their flavor and high nutritional value.
Mushrooms are rich sources of important groups of nutrients that we need. A study shows an average mushroom has:
- 88-90% water
- 3-8% proteins
- 4-9% carbohydrates
- 0-3% fat, most of which is polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA)
- 1-2% of minerals and vitamins
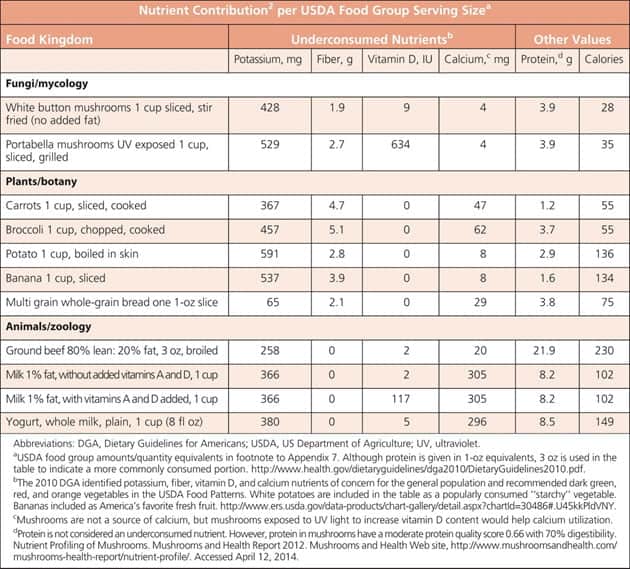
(Image credits: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4244211/)
Ways to Consume Mushrooms
Mushrooms are part of cuisines all over the world. You can find common and affordable to rare and expensive ones.
Preparation and cooking method can affect the benefit you get from your mushrooms.
Much of the nutrients can be present in cap peel. So, if you are sure the mushrooms are free of pollutants, it is best not to peel them. People dry mushrooms to store them for a longer time. Soak them in water before cooking them.
You can eat mushrooms raw. But, cooking for short periods is better for your health. Cooking does not affect levels of antioxidants like ergothioneine, glutathione, and complex sugars. Grilling or microwaving with a little oil, is better than cooking or frying. It increases antioxidant levels.
The umami or savory taste of mushrooms makes it an ideal substitute for meat in any dish. You can replace ground meat with mushrooms, without loss of taste and texture. Here again, the cooking method is crucial.
Besides eating mushrooms, you can also make drinks from them. This is especially popular in use for medicinal purposes. Cook or seep them in water to make tea and coffee.
You can find medicinal mushrooms, dried and powdered, and packaged in capsules.
Health Benefits of Mushroom Consumption
All this information about mushrooms is good. But are you wondering what this can mean for you?
We are listing the possible health benefits of mushrooms.
We call them possible because there hasn’t been enough research. We need more studies to be sure of the health benefits mentioned in folklore.
Mushrooms have several medicinal properties. They do this by improving our immune system.
1. Mushrooms Improve Immunity
Mushrooms improve our immune systems due to their antioxidant property.
Reduce Free radicals
We need antioxidants to reduce the number of free radicals in our bodies. When our body processes food, it produces free radicals. These are lone oxygen atoms, with a missing electron.
Some number of free radicals is normal and even good for the body. But, too many free radicals cause oxidative stress. The free radicals attack other chemicals because they are trying to find an electron. Human bodies produce antioxidants to control the levels of free radicals. These antioxidants give the free radicals, the electron they need to neutralize them.
But, the free radicals can accumulate over time. They travel within the body attacking proteins, fats, and DNA in cells. As a result, our immune system suffers. We can develop chronic problems and become susceptible to infections.
Accumulated free radicals cause many problems associated with old age. These could be Alzheimer’s, heart diseases, cataracts, cancer, and arthritis.
Free radicals are also responsible for aging, as they destroy cells.
Mushrooms have many substances that act as antioxidants:
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Secondary Metabolic Compounds
Minerals
Mushrooms are rich sources of many minerals that are antioxidants. These are:
- Selenium
- Manganese
- Magnesium
- Zinc
- Copper
- Iron
The amounts of minerals present will depend on the species.
Selenium is of particular interest, we as need it. Many people show a deficiency of this mineral. It acts as a catalyst to produce oxidants that control damage due to hazardous compounds. Some wild mushrooms are rich sources of selenium, but not the cultivated varieties. You can increase selenium in cultivated mushrooms, by adding it to the substrate it is being grown on.
Wild mushrooms like Amanita strobiliformis and Boletus edulis have a lot of selenium.
Besides selenium, other minerals also act as antioxidants. Our body needs the elements for many roles. These are magnesium, copper, and zinc. Mushrooms, such as morels, oysters, enokis, and bolete are rich sources of them.
Vitamins
Several vitamins in mushrooms, such as vitamin A, and C, also act as antioxidants. Among them, vitamin A is very active, as it can cross into our blood and make its way into the nervous system. Its deficiency can cause Parkinson’s disease and vascular dementia. Vitamin A is abundant in pinkish-red Cantharellus cinnabarinus and orange C. friesii. So much so that ancient Chinese medicine used them to cure night blindness.
Vitamin C is another antioxidant, whose levels in our body fall as we grow older. Smoking or exposure to UV light and pollutants will also reduce vitamin C levels. Dietary sources are the best way to do supplement this loss. Mushrooms are the ideal choice. There is more vitamin C in mushrooms than in citrus fruits! Or any other fruit or vegetable. Wild mushrooms have more vitamin C than the cultivated varieties.
Complex Sugars
Polysaccharides are not only antioxidants. They also strengthen the immune system by other actions. For example, soluble beta-glucans. You will find them in high concentrations in reishi (Ganoderma lucidum).
They prevent infectious diseases and tumor growth.
Secondary Metabolic Compounds
Secondary metabolic compounds are other groups of antioxidants in mushrooms. These can be compounds like polyphenols, steroids, terpenes, and carotenoids.
Polyphenols, include tannic acid, gallic acid, and catechin. They reduce free radicals and improve cell survival. Turkey tail mushrooms (Trametes versicolor) rich in phenol and flavonoid could boost immunity.
Flavonoids are another group of phenols. They scavenge free radicals. They also inhibit enzymes that produce free radicals. So, they are can also be preventive in action.
Ergothioneine and glutathione are present in unusual amounts in mushrooms. Penn State researchers say mushrooms are the richest source of the two antioxidants. They help against aging and improve health. All the species of mushrooms do not have the same levels of the two antioxidants. Porcini (Boletus spp.) have the highest levels of these two antioxidants. Button mushrooms have less. But it is still more than what you would get from eating other types of foods.
Support Your Immune System
Other medicinal roles of mushrooms also improve your immune system:
- Shiitake and maitake generally improve immune systems
- Chaga mushrooms (Inonotus obliquus), will help you fight infections from viruses, bacteria, and other microbes. They can also help against inflammation
2. Healthy Life
We can use the vitamins in mushrooms to stay healthy in many ways.
Vitamin B
Vitamin B complex is necessary for a healthy body. Pantothenic acid or vitamin B5 helps our body process food to produce energy. We need Vitamin B9 to produce red blood cells. Mushrooms can be a rich source of the following vitamin B
- B-1 or thiamine
- B-2 or riboflavin
- B-3 or niacin
- B-5 or pantothenic acid
- B-9 or folate
Vitamin D
You also find vitamin D – D2, D3, and D4 in mushrooms. Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) help absorb calcium and phosphorus. It is necessary to prevent bone loss and for kidney functioning. We need this vitamin for bone stability, muscle function, and insulin production. It helps us against cardiovascular diseases and cancer, besides improving our immunity.
All mushrooms will not have vitamin D, especially if the cultivated ones. There is little vitamin D in white button, cremini, portabella, and enoki. This is because they are grown in the dark. UV (ultraviolet) radiation during cultivation help. It can increase vitamin D2 in mushrooms and to some extent also D3.
Shiitake and oyster have moderate amounts. Morel, chanterelle, maitake, and shiitake mushrooms have higher amounts of vitamin D2.
3. Eat Mushroom to Lose Weight
You can reduce dietary calories and fat, to lose weight, if you substitute meat with mushroom. Its high dietary fiber content also helps in this case.
In a randomized scientific trial, people compared mushrooms to beef. They ate 4 lunches with mushrooms on consecutive days, and 4 lunches with beef. They gave similar ratings for mushrooms and meat for satiation, palatability, and appetite. Since the calorie content of mushrooms (339 kcal) is half of the beef (783 kcal), dieters can get a clear benefit.
You could call mushrooms low energy density food, which is good for people who want to diet.
4. Suitable for Hypertension and Diabetes Patients
People who have hypertension and diabetes could consider mushrooms in their diet, because,
- Mushrooms are low in sodium, which causes hypertension. The best mushrooms for reducing hypertension are enokis
- Mushrooms have a low glycemic index, and high mannitol. This is better for diabetic patients. Oyster and turkey tail mushrooms are ideal
- The high dietary content in mushrooms also helps against diabetes
5. Live Longer
Eating mushrooms can bring down the levels of free radicals. This is due to the many groups of antioxidants. as a result, you reduce the chances of getting many diseases that occur in old age. That makes you healthier. It also gives you a better quality of life and could increase your longevity. Scientists are trying to establish if Reishi mushrooms can extend the human lifespan.
Mushrooms could reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. This could happen due to the effect of ergothioneine and glutathione.
6. Cancer Supplements
The antioxidant action by mushrooms could help prevent many cancers. Some useful mushrooms to consider are:
- Reishi and Vitamin D for cancer patients
- Chaga for protection against DNA damage
7. Heart problems
Mushrooms could benefit heart patients in many ways. Mushrooms reduce cholesterol, provide vitamin C, beta-glucans, potassium, and fiber. All are good for the heart.
- Shiitake mushrooms rich in beta-glucans could control hypertension and cholesterol
- Potassium in mushrooms, which lowers blood pressure, is abundant in common white mushrooms
- Oyster and shiitake are good as they have the highest fiber content among mushrooms
8. Improve Cognitive Powers
Antioxidant-rich mushroom varieties could stimulate our brain and help in nerve growth. As a result, we could be able to improve the ability to learn, remember, focus, and in problem-solving. Using Reishi mushrooms can help in cognitive functions.
Foraging Wild Mushrooms
Wild mushrooms are generally more nutritious than cultivated ones. And foraging for mushrooms is part of many traditions globally.
Yet, it is better to stick to commercial varieties, if you are not an expert in identifying mushrooms. Many mushrooms look alike. Most mushrooms are poisonous and it is hard to tell them apart from the edible species.
- Poisonous mushrooms can cause severe distress like nausea, vomiting, cramps, convulsions, and insanity
- About 70-80 species can even be lethal. People have died after eating a small quantity of these mushrooms
Also, when mushrooms grow in the wild they will absorb many pollutants in the soil, water, and air. Heavy metals on mushrooms can be toxic.
So, buy canned wild mushrooms available in supermarkets, which come from reliable sources.
Be Sustainable
Mushrooms are becoming more popular. People want to switch from meat to a vegetarian or vegan diet. It could be for health reasons or to protect the environment. As mushrooms are nutrition-rich, this has several benefits for people. Keep in mind that buying local food is also important. So, buy mushrooms that come from your region. That is better than buying exotic varieties. People import them halfway across the globe. In the end, a balanced diet including many food groups is best for you.

